
- #Calculating rate of return on future cashflows how to
- #Calculating rate of return on future cashflows series
You can estimate each year's net cash flows by adding the expected cash inflows from projected revenues to potential savings in labor, materials and other components of the initial project cost. To use the NPV calculation formula, include the following variables: Annual net cash flows

Related: Internal Rate of Return: IRR Definition and How To Calculate It Variables in the NPV formula NPV = sum of the present value of expected cash flows - initial investment Here's the NPV formula for a longer-term project with multiple cash flows: The formula for longer-term investments with multiple cash flows is almost the same, except you discount each cash flow individually and then add them together. 2. NPV formula for a project with multiple cash flows and a longer duration In this formula, "i" is the discount rate, and "t" is the number of time periods. When calculating the NPV for a short-term project with a single cash flow, the only variables required to get the present value are the cash flow, the cash flow period and the discount rate. Here's the NPV formula for a one-year project with a single cash flow: NPV formula for an investment with a single cash flow There are two NPV formulas typically used, including: 1. This means the formula for calculating the NPV for a short-term project with one cash flow differs from that of a multiyear investment with multiple cash flows. It also depends on the investment's intervals and number of future cash flows. Unlike the internal rate of return (IRR), the NPV calculation formula requires a discount rate. The NPV formula is a method of determining the profitability of an investment by discounting the future cash flows of the investment to today's value.
#Calculating rate of return on future cashflows how to
In this article, we discuss the NPV formula, list the variables to include in the formula, explain how to calculate NPV and provide example calculations. Capital budget planners might find NPV useful because it provides results in dollar values and can be a fair indicator of an investment's profitability. NPV allows you to use present values to determine the potential future earnings of a project.
#Calculating rate of return on future cashflows series
PV, of a series of cash flows is the present value, at time 0, of the sum of the present values of all cash flows, CF.Net present value (NPV) is a capital budgeting technique used to estimate the current value of the future cash flows that a proposed project or investment may generate. Payments at Period Beginning or End Choose if payments are made at the beginning of each period (like an annuity due in advance) or at the end of each period (like an ordinary annuity in arrears) Cash Flows The cash flow (payment or receipt) made for a given period or set of periods. You might have a yearly rate and compounding is 12 times per yearly period, monthly. Compounding is the number of times compounding will occur during a period. Rate per period This is your discount rate or your expected rate of return on the cash flows for the length of one period.
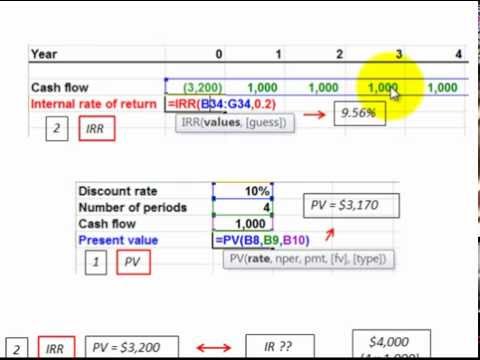
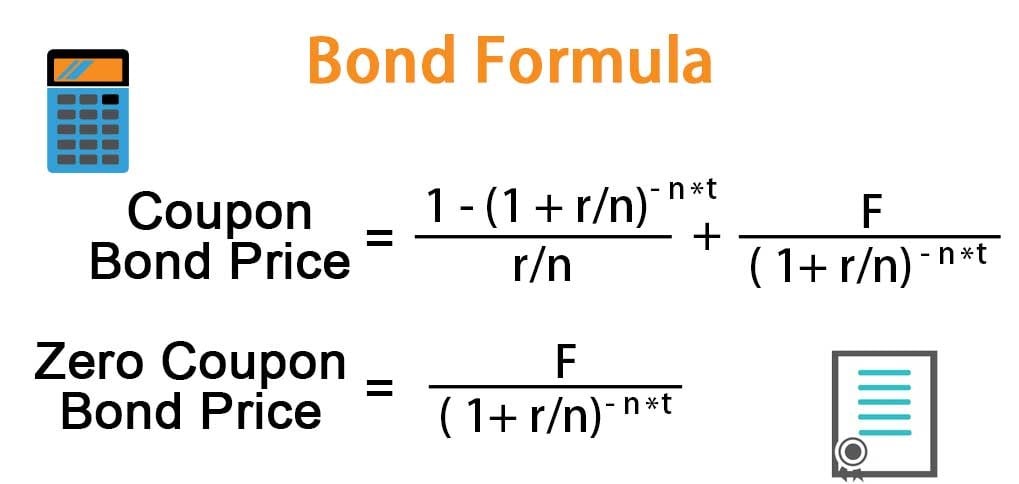
Just be sure you are consistent with weeks, months, years, etc for all of your inputs. Commonly a period is a year or month. However, a period can be any repeating time unit that payments are made. Periods This is the frequency of the corresponding cash flow. To include an initial investment at time = 0 use Present value of uneven cash flows (or even cash flows). Calculate the present value ( PV) of a series of future cash flows.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
